

Library > Sonography > Echocardiography > Electrocardiogram (ECG) 12-Lead
Try Simtics for free
Start my free trialElectrocardiogram (ECG) 12-Lead
Materials Included:
-

-

-

-

-

Check our pricing plans here
Unlimited streaming.
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a method to graphically display the electric current generated by the heart muscle during a heartbeat. This SIMTICS module teaches you how to prepare for, record and interpret a 12-lead ECG. The interactive simulator lets you learn and practice how to record an electrocardiogram, and how to interpret the heart rate and rhythms for common pathologies. Online simulations offer a safe practice environment and also enable you to try out procedures that you might not otherwise experience. This module is ideal if you are studying for the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS) registry exams.
You’ll learn
- to practice, perfect and test your skills in setting up, recording and interpreting a 12-lead ECG
- to better visualize and understand the anatomy and physiology of the heart, with our 3D model and illustrations
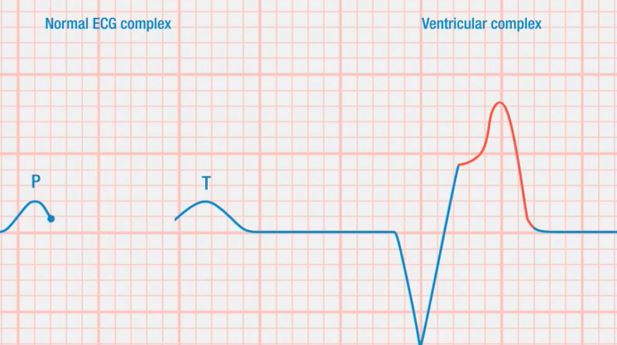
- how to determine the heart rate and identify different heart rhythms on the ECG strip: atrial, junctional, ventricular, and pacemaker rhythms, and AV blocks
- about stress testing and Holter monitoring
- much more (see Content Details for specific information)
- Describe the anatomy and physiology of the heart
- Identify the basic electrophysiology of the heart
- Describe the sinus mechanisms
- Describe atrial rhythms
- Describe junctional rhythms
- Describe ventricular rhythms
- Describe atrioventricular (AV) blocks
- Describe pacemaker rhythms
- Explain and demonstrate the 12-lead ECG
- Describe stress testing and Holter monitoring
The SIMTICS modules are all easy to use and web-based. This means they are available at any time as long as the learner has an internet connection. No special hardware or other equipment is required, other than a computer mouse for use in the simulations. Each of the SIMTICS modules covers one specific procedure or topic in detail. Each module contains:
- an online simulation (available in Learn and Test modes)
- descriptive text, which explains exactly how to perform that particular procedure including key terms and hyperlinks to references
- 2D images and a 3D model of applied anatomy for that particular topic
- a step by step video demonstration by an expert
- a quiz
- a personal logbook that keeps track of all the modules the learner has studied and how long
For more details on features and how your students can benefit from our unique system, click here.









